Imaging studies can be very useful for rehabilitation professionals in assessing, diagnosing, and treating their patients. Some of the commonly used imaging modalities in physical therapy include X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound.
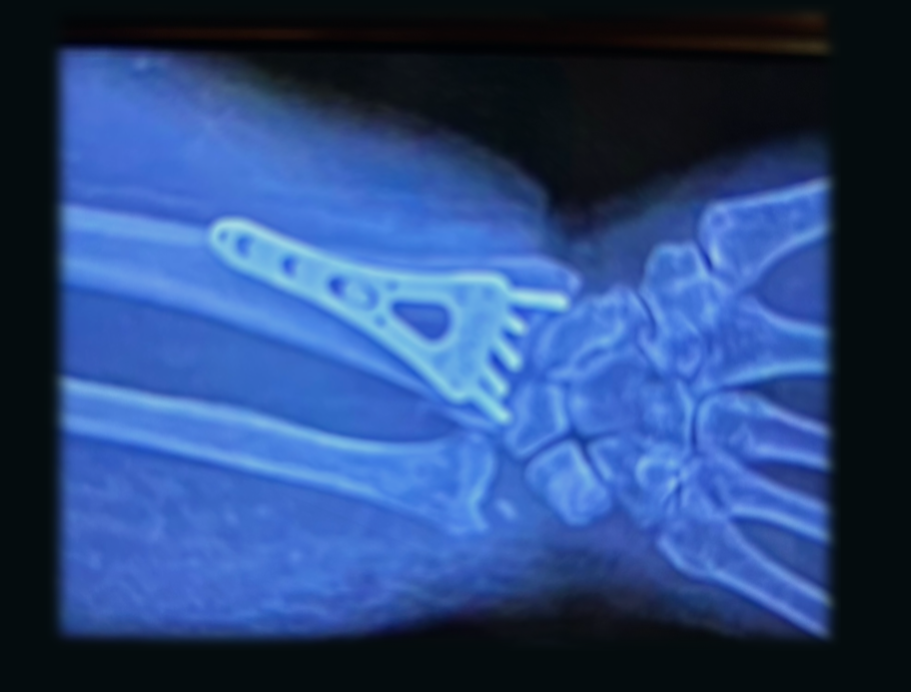
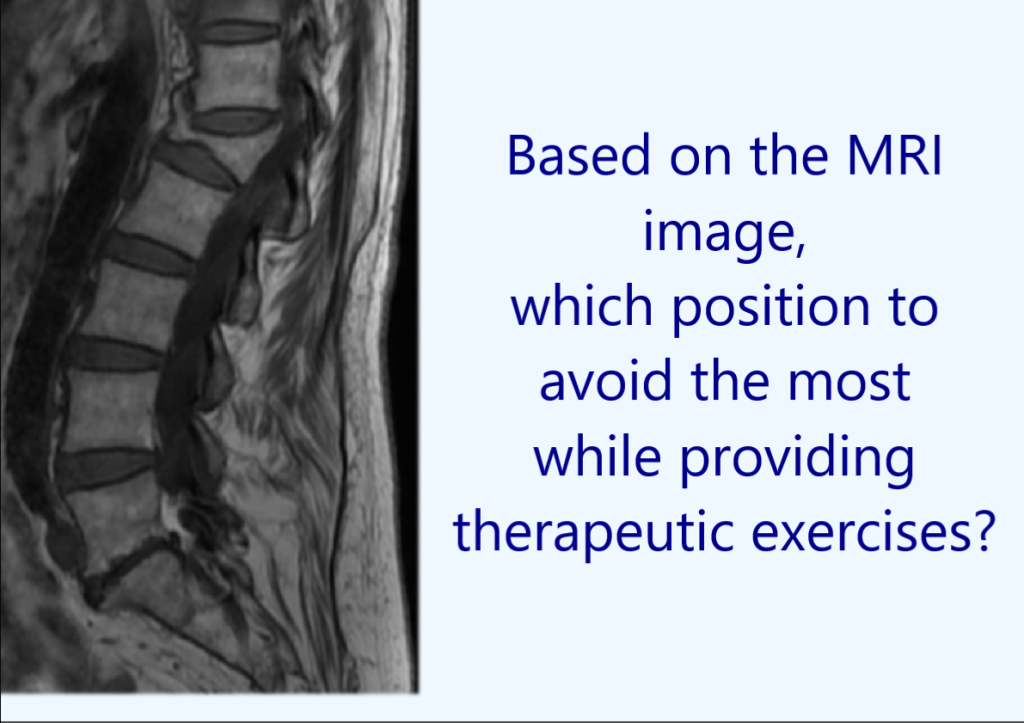
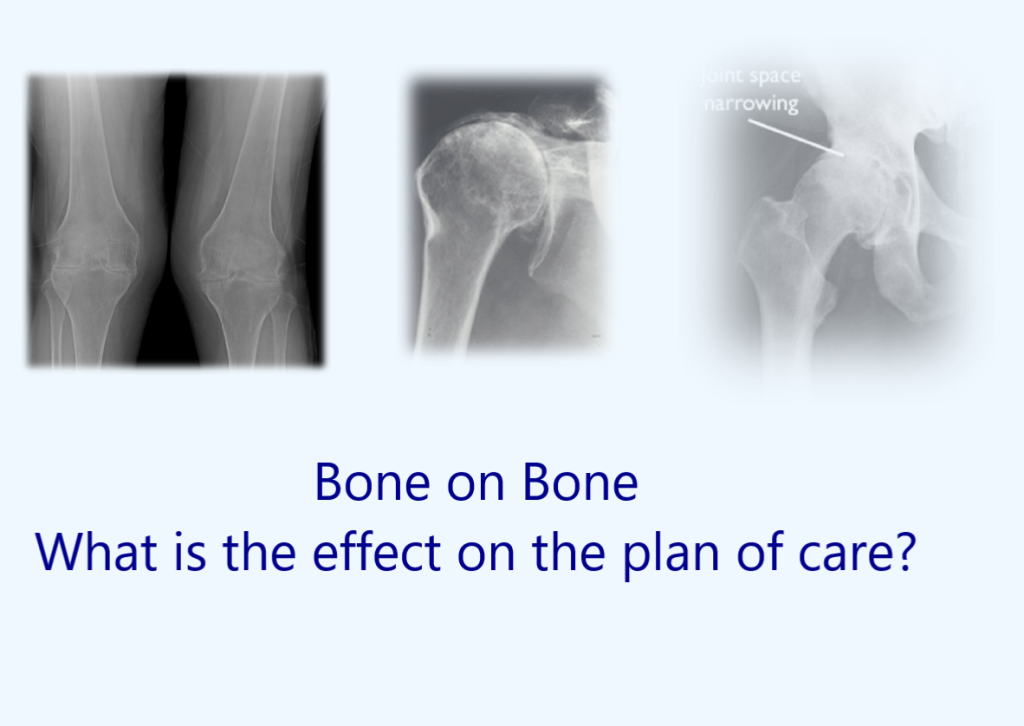
X-rays are useful in detecting fractures, dislocations, or bone abnormalities. CT scans and MRI are helpful in identifying soft tissue injuries such as ligament tears, muscle strains, and joint damage. These imaging modalities also provide a better visualization of the spinal cord, nerve roots, and intervertebral discs.
Ultrasound is useful in evaluating muscles, tendons, and ligaments in real-time, allowing for precise and targeted treatment.
While imaging studies can greatly benefit rehabilitation professionals in their treatment of patients, it is important to note that they should not be solely relied upon. A thorough clinical examination and appropriate functional testing are still crucial in developing an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Research suggests that rehabilitation professionals may use the image of the healing joint to determine treatment goals with regard to joint mobility or abnormal kinematics of the injured joint and adjacent joints. The viewing of radiologic studies by the rehabilitation professionals could enable greater insight into the patient’s pathology and possibly lead to the alteration of rehabilitation strategies.
This course will provide case studies to illustrate the importance of imaging studies in rehabilitation professionals daily practice.